Thermal Technology
Green Extraction Thermal TechNOLOGY
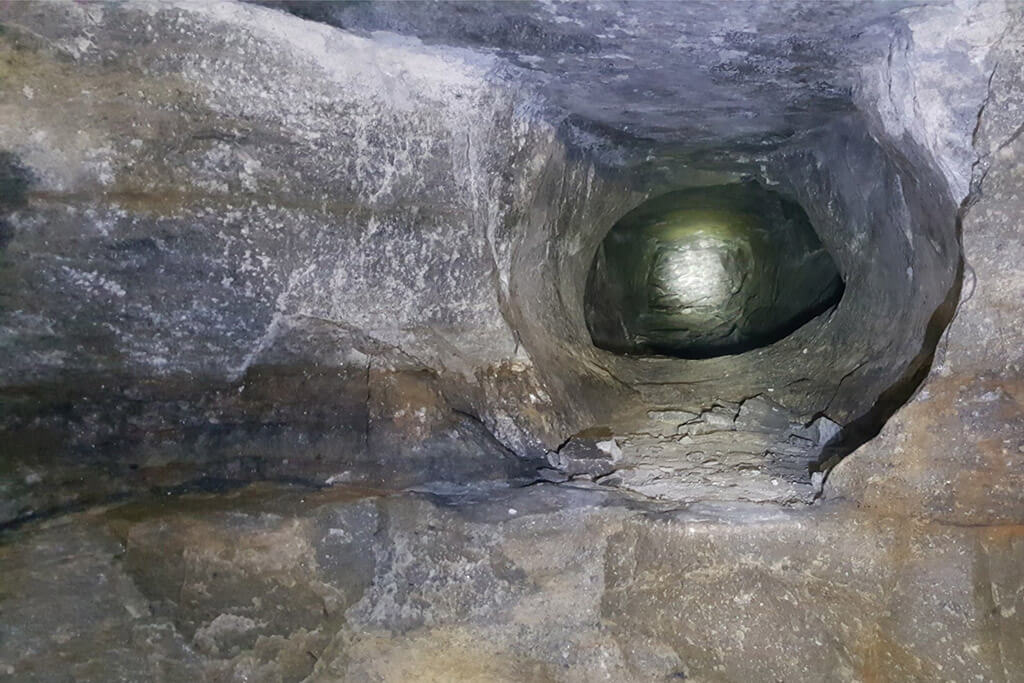
A patented mining method that uses thermal energy applied inside a drilled pilot hole to introduce micro stress fractures into the surrounding rock which allows a spalling process to remove this rock in small chips. Therefore, enlarging the pilot hole’s diameter.

Safety
- No need for people to go into narrow stopes.
- Hardly any explosives with their related safety concerns.
- No potential for explosives damage to surrounding rock, blast cracks disturbing hang wall and related FOG safety issues.
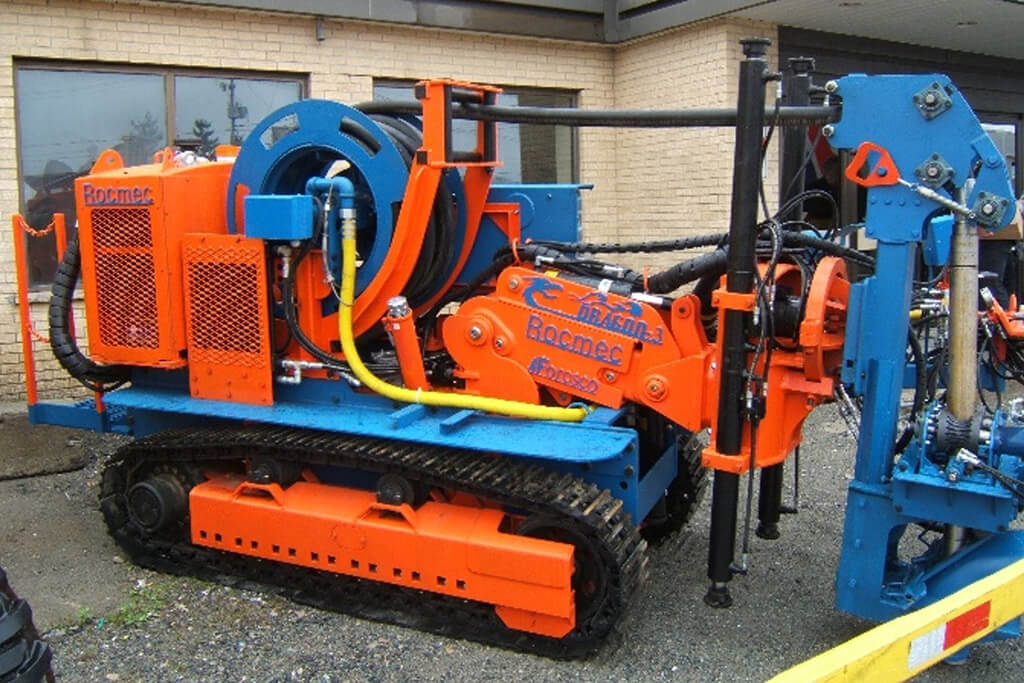

Grade
- Less dilution
- Precision extraction

Efficiency
- Less ore to be moved UG and less crushing,
- Significant reduction in dilution translates it to many advantages such as, smaller drifts, hoists, etc.

Continuous
- No need for blast re-entry times.

Economical
- All the above = less costs overall
KEY ADVANTAGES
Reducution in mining dilution
- Less volume, higher grade, more ounces
- Continuous possible (no blasting)
- Establishment of a free face for blasting operations
- Significant reduction in blast induced damage
Integrated into conventional mining methods
- Fast productivity (4 to 8 spalled meters per hour)
- Spalled chips generated are small (5-20mm)
- No need for primary crushing
- Can be hydro transported
Hole length flexibility up to 25m
- Equipment required is small, simple, and effective
- Hole flexibility from 20cm to 80cm diameter
- Hole diameter can be changed within one hole
- No additional consumables required
Thermal mining method improves safety by moving people away from the exposed span where falls-of-ground are more likely; improves productivity by eliminating re-entry periods mandated when using explosives; reduces dilution by extracting only the ore; and has the potential to increase reserves by making it possible to mine pillars and other isolated blocks-of-ground that may not be economically viable to mine with other methods.
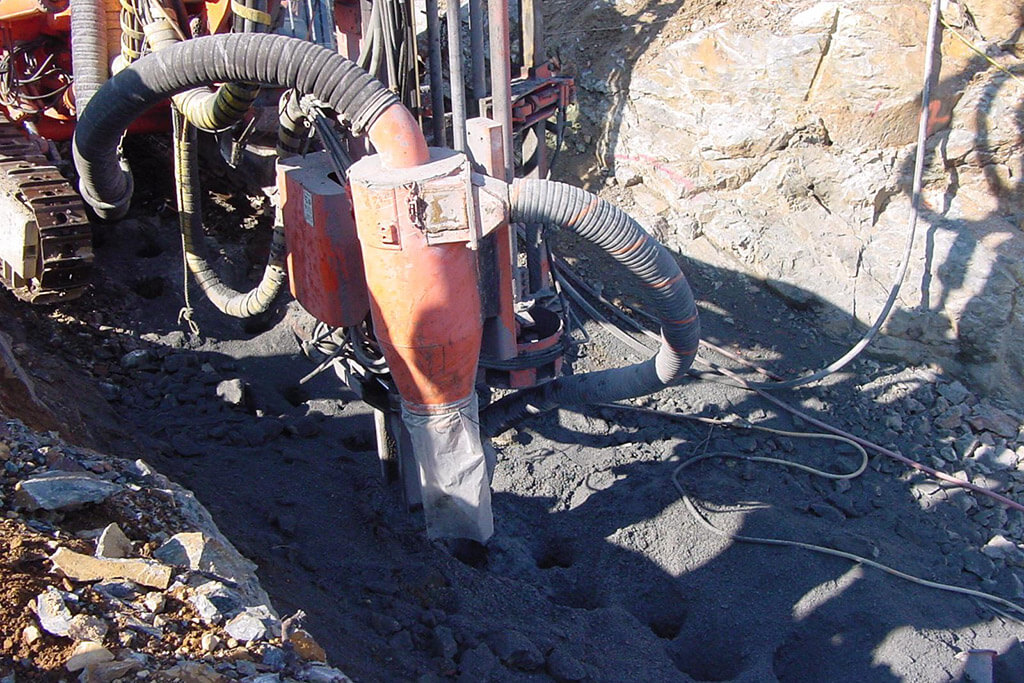
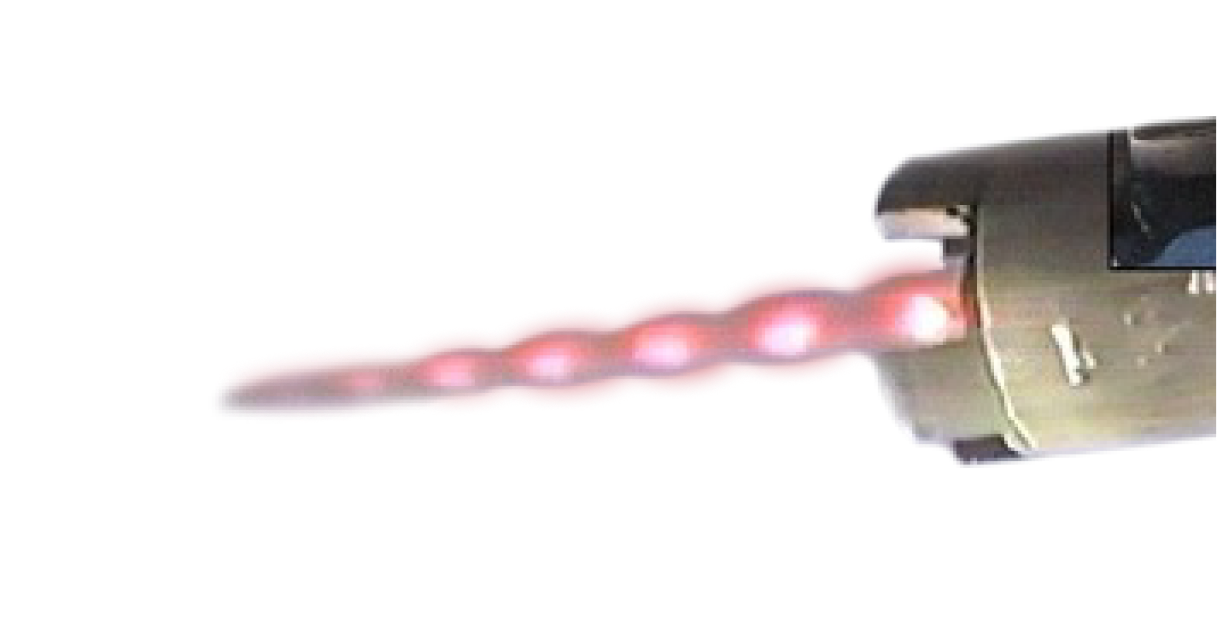
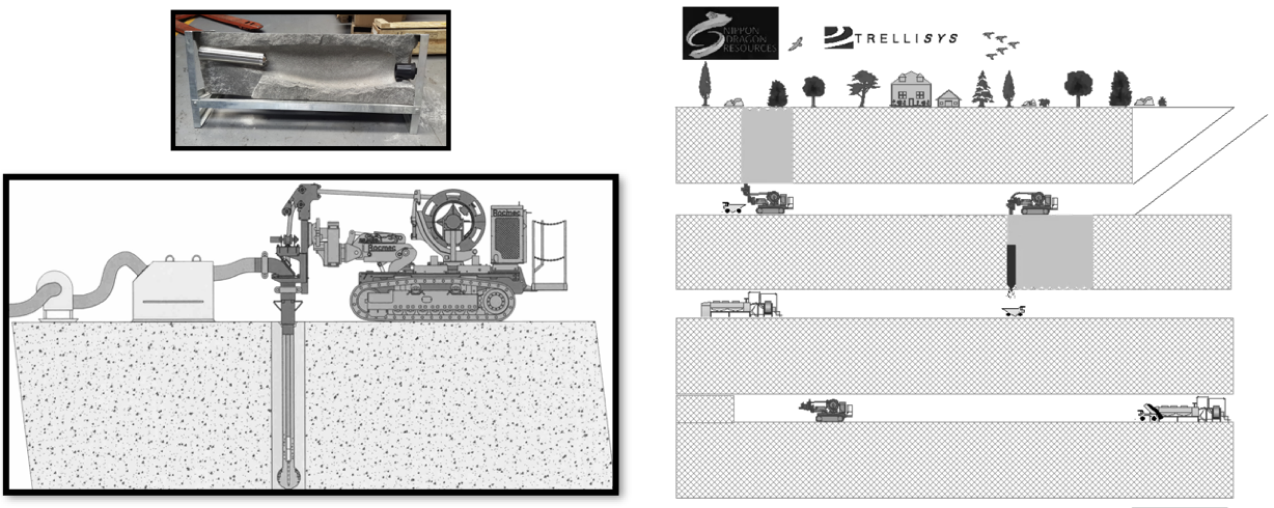
The mining method involves drilling holes within a vein structure, inserting a thermal lance to apply high temperatures inside the hole. The rock then spalls and approximately 30 % of the chips are flushed out of the hole while spalling, with the remaining 70% being cleaned out afterwards.

HOW IT WORKS
1.
Thermal Fragmentation
- A mining method that uses heat to shatter/spall high-grade narrow ore bodies, greatly reducing the use of explosives.
- Extracting the vein with minimal dilution.
- Could be employed as a stand-alone method or as the perfect complement to any conventional mining operation.


2.
Precision Mining
- The art of creating openings of various diameters economically and safely.
- Conclusive tests of hard rock fragmentation conducted around the globe.
- Thermal fragmentation is a highly-precise mining method for creating large openings and extracting ore.
3.
Surgical Precision
- Enlarges a 15cm hole up to 80cm and as much as up to 110cm in a very good ground condition.
- Operates at any angle and dip, up to 25 metres
- A 100 cm diameter hole can produce between 8-10 tonnes per hour
- Using control blasting between holes can multiply the per tonne/per hour productivity
RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT
An extensive R&D programme is currently ongoing and will continue for the foreseeable future. Participants involved in the programme:
– COALIA/College center for technology transfer/Thetford Mines College
– LBM Quebec
– Nemesis Intelligence
– SEMM Geoservices
– Goldminds Geoservices
– MaXem (South Africa)
The objectives of the programme include but are not limited to:
– Enhance performance of the thermal units;
– Geology rock identification and fragmentation controlling factors;
– Effective fragmented rock recovery process;
– Spallability index to classify fragmentability vs sample geology:
– Categorisation/quantification of fragmentated ore ‘chips’ (weight, quantity, shape etc) produced by Spallability tests in order to standardize testing in South Africa and Canada;
– In situ rock characterisation and geology identification prediction;
– Development of measuring devices for fragmented hole characterisation;
– Development of a scanning device for small and irregular fragmented holes to provide a 3D
image to calculate production, evaluate fragmentation quality/quantity and geology;
– Developing a 3D web/Cloud based viewing application to visualize fragmented hole, calculate
performance;
– In hole imaging and predictive rock composition and localisation in drilled holes;


